
There is a graphical benchmark called gnome-disks contained in the gnome-disk-utility package that will give min/max/ave reads along with average access time and a nice graphical display. Note: One should run the above command 2-3 times and manually average the results for an accurate evaluation of read speed, per hdparm(8) § T. Timing buffered disk reads: x MB in y seconds = z MB/sec Timing cached reads: x MB in y seconds = z MB/sec This method is independent of partition alignment! Using hdparm with the -Tt switch, one can time sequential reads. Storage media can be benchmarked with hdparm ( hdparm). time contains the time command and some shells provide time as a builtin command. The time(1) command provides timing statistics about the command run by displaying the time that passed between invocation and termination. Iperf can be installed, or a different version of iperf is available with iperf3.
It has nicely formatted output and a parallel test mode. Iperf is an easy to use point-to-point bandwidth testing tool that can use either TCP or UDP. Various flavors of ttcp can be found in the AUR: The program must be provided on both nodes between which bandwidth is to be determined. Ttcp (Test TCP) measures point-to-point bandwidth over any network connection. Interbench is available in the AUR: interbench AUR. Tip: With careful benchmarking, different hardware can be compared. It is designed to measure the effect of changes in Linux kernel design or system configuration changes such as CPU, I/O scheduler and filesystem changes and options. Interbench is an application designed to benchmark interactivity in Linux.
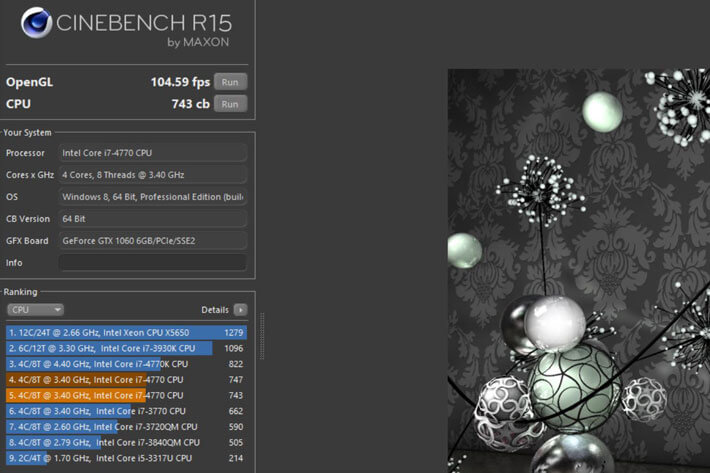
#BENCHMARK CPU SOFTWARE INSTALL#
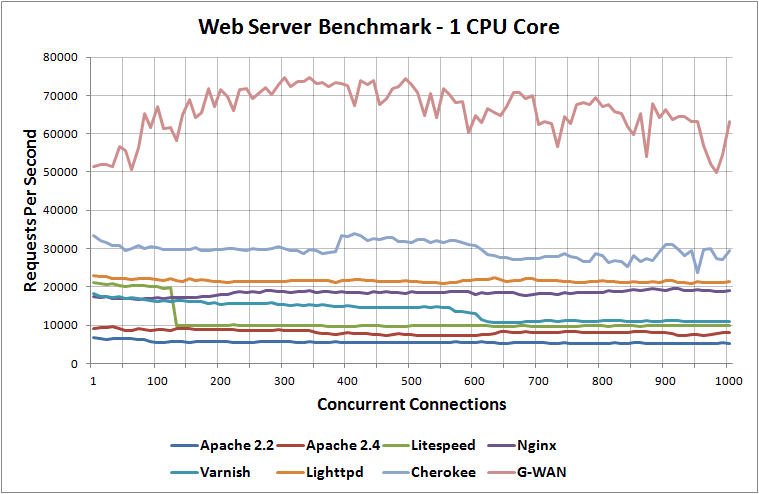
Install unixbench AUR, to run the benchmark run ubench. Many tools can be used to determine system performance, the following provides a list of tools available.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
